Analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid metatranscriptomes among patients with COVID-19 disease | Scientific Reports
Comparison between subject categorical classes (i.e., uninfected controls, or patients with CAP or COVID-19 disease)
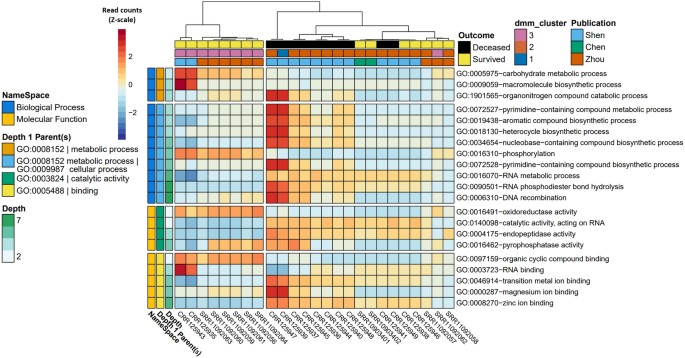
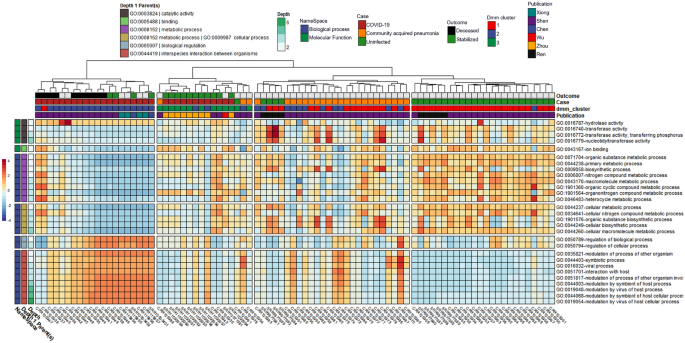
After controlling for random effects of publication and patient, results from the MaAsLin2 comparison across individual subjects were grouped by one of three categorical classes: (1) uninfected controls; (2) CAP patients; or (3) COVID-19 patients with moderate to severe disease, including death (Table 1). This revealed 20 out of 13,534 GO terms associated with COVID-19 when compared to the CAP cohort and 30 out of 13,534 GO terms associated with COVID-19 when compared to the uninfected cohort (Fig. 1, Tables 1 and 2). Significant GO terms were grouped under seven parental GO terms, including catalytic activity [GO:0003824], binding [GO.0005488], metabolic process [GO:0008152], cellular process [GO:0009987], biological regulation [GO:0065007], viral process [GO:0016032], and interspecies interaction between organisms [GO:0044419] (Fig. 1, Suppl. Table 3). Parental GO terms have smaller depth numbers (e.g., depth = 1) in the Gene Ontology hierarchy and represent higher-level features under molecular function [GO:0003674] or biological process [GO:0008150], whereas larger depth numbers represent nodes in the ontology tree that are lower and refer to more specific functions or processes.
Heatmap with notable microbially-derived gene ontology functional annotations associated with COVID-19 (n =32), as compared to community acquired pneumonia (n = 29) & uninfected (n=25) cohorts. Cells are colored via z-scale calculations of the total read counts for each GO term by sample. Rows are sorted by parental GO terms (depth = 1), and columns are clustered by Euclidean distance using ward D2 clustering. Comparisons were conducted using MaAsLin2, controlling for publication and patient ID with Benjamini Hochberg multiple test comparison (q < 0.05).
GO terms enriched in the COVID-19 cohort compared to the uninfected cohort included hydrolase activity [GO:0016787], as well as all significant GO terms with the parental terms of biological regulation [GO:0065007], viral process [GO:0016032], and interspecies interaction between organisms [GO:0044419]. Hydrolase activity [GO:0016787], nucleic acid metabolic process [GO:0090304], and many GO terms classified under interspecies interaction between organisms [GO:0044419] were also enriched in the COVID-19 cohort when compared to CAP. In contrast, GO terms enriched in the uninfected cohort compared to the COVID-19 cohort included all significant GO terms with the parental terms of cellular process [GO:0009987], metabolic process [GO:0008152], binding [GO.0005488], and terms classified under catalytic activity [GO:0003824] other than hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]. Results from the Dirichlet multinomial mixtures clustering analysis using all 13,534 gene ontology counts resulted in a best model fit using three distinct clusters that were significantly associated with each case cohort [p < 0.0001] (Fig. 1, Suppl. Table 5).
Taxonomic comparisons of the COVID-19 cohort to uninfected and CAP cohorts revealed 233 and 61 significantly differentiated species-level taxa with absolute values of log2 median ratios > 1.0 when comparing the COVID-19 cohort to uninfected and CAP cohorts, respectively (Suppl. Table 6). All significant taxa found in the CAP cohort were depleted compared to the COVID-19 cohort. Additionally, all significant taxa found in the CAP to COVID-19 comparison were also identified as significant in the uninfected to COVID-19 comparison (Suppl. Table 6). Of the taxa identified when comparing the uninfected cohort to the COVID-19 cohort, a total of 36 species were only marginally enriched (Suppl. Table 6).
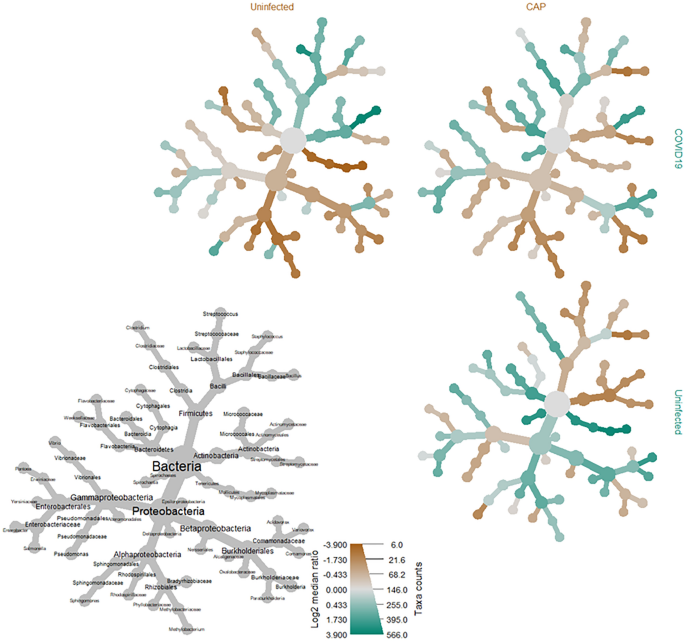
Taxonomic comparisons resulted in a statistically significant difference amongst several microbial genera within the phylum of Proteobacteria, including those of the families Sphingomonadaceae (i.e., Sphingobium, Sphingopyxis, Sphingomonas) and Rhodobacteraceae (i.e., Paracoccus) when comparing the COVID-19 cohort to the uninfected (p < 0.001, q < 0.001) and CAP (p = 0.0067, q = 0.024) cohorts (Fig. 2, Table 4). There was a significant increase in several species belonging to the genus Sphingomonas among BALF specimens from COVID-19 patients when compared to both the uninfected (p < 0.0001, q < 0.001) and CAP cohorts (p < 0.005, q < 0.05) (Suppl. Table 6), with a more significant increase of Sphingomonas in COVID-19 patients when compared to the uninfected cohort than to the CAP cohort (Fig. 2). An analysis of the most common SeqScreen outputs taxonomically classified as Sphingomonas in BALF specimens among patients with COVID-19, irrespective of disease outcomes, included GO term assignments of hydrogen peroxide catabolic process [GO:0042744], response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979], catalase activity [GO:0004096], heme binding [GO:0020037], and metal ion binding [GO:0046872].
Heat tree matrix visualizing distinct COVID-19 vs. uninfected & community acquired viral pneumonia taxonomic profiles. This taxonomic heat tree data matrix visualization depicts the log2 median ratio differences across the three different cohorts. The tree depicted in grey in the lower left represents a taxonomic assignment key for all the other trees. Each of smaller trees represents a comparison between the different cohorts, as labelled in the columns and rows. The taxa colored brown are more abundant among the cohort labelled in the columns, whereas taxa colored green are more abundant in the cohort labelled in the rows. For example, there were significant increases (green) identified in log2 median ratio of several species belonging to the genus Sphingomonas when comparing the COVID-19 to the uninfected cohort (top left) and decreases (brown) when comparing the uninfected cohort to the community acquired pneumonia (CAP) cohort (bottom right).
There were no significant differences in alpha diversity when comparing case type (i.e., COVID-19, CAP, uninfected) (p-value = 0.051) or mortality (p-value = 0.8918) using the Shannon and inverse Simpson indices31,32. A full list of diversity metric indices is available in Supplementary Table 7. Beta diversity analyses did not reveal any statistically significant within group differences (F = 0.293, p = 0.747) by cohorts, which were determined by analysis of variance homogeneity of multivariate dispersions based on Euclidean distance. Further, no significant differences were observed in beta diversity amongst case type (F = 2.9257, p > 0.05) or mortality (F = 3.5978, p > 0.05), as determined by the permutation test for adonis using bray Curtis dissimilarity indices after stratifying by publication and patient.
Metatranscriptomic comparison of BALF specimens from COVID-19 subjects sub-categorized and stratified by disease survival or death
From subjects with known COVID-19 survival outcomes (i.e., of 32 samples, n = 10 deceased, and n = 15 survived), a stratified analysis amongst the categorical class of COVID-19 disease was performed via MaAsLin2. After controlling for random effects of patient, we observed 21 unique GO terms which were significantly increased in their association with death (n terms = 16, q-value < 0.05) or survival (n terms = 5, q-value < 0.05) from COVID-19 disease, with parental GO terms (depth = 1) of metabolic process [GO:0090304], binding [GO.0005488], and catalytic activity [GO:0003824] (Table 5, Fig. 3). GO terms with significant q-values (< 0.05) that were terminal in the observed GO term lineage (i.e., as specific as possible within the lineages of our result set), included nucleobase-containing compound biosynthetic process [GO:0034654], organonitrogen compound catabolic process [GO:1901565], pyrimidine-containing compound biosynthetic process [GO:0072528], and DNA recombination [GO:0006310] classified under the parental GO term of metabolic process [GO:0008152]; RNA binding [GO:0003723], magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287], and zinc ion binding [GO:0008270] classified under the parental GO term of binding [GO.0005488]; and oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491] and endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175] classified under the parental GO term of catalytic activity [GO:0003824] (Suppl. Tables 4, 9–17).
Heatmap of significantly different gene ontology terms associated with COVID-19 mortality comparing deceased (n = 10) versus survived (n = 15). Cells are colored via z-scale calculations of the total read counts by sample (x axis) and by GO term (y axis). Rows are sorted by parental GO terms (depth = 1) and columns are clustered by Euclidean distance using ward D2 clustering. Comparisons were conducted using MaAsLin2, controlling for patient ID with Benjamini Hochberg multiple test comparison (q < 0.05).
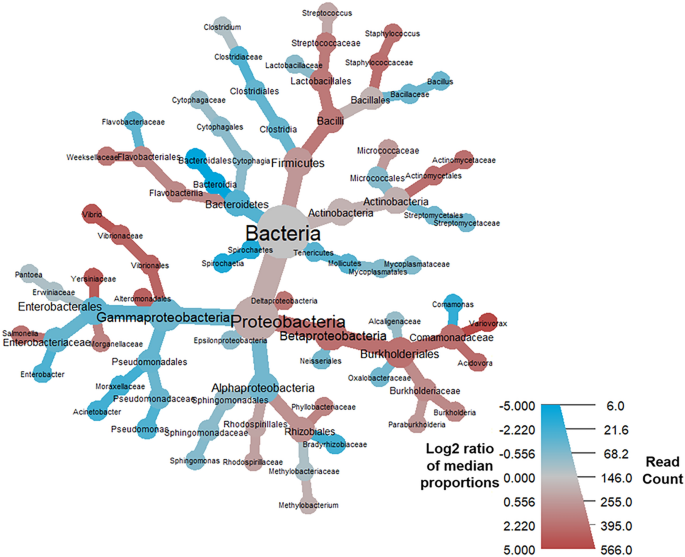
Of the nine terminal GO terms that were significantly different in this analysis (q-value < 0.05), RNA binding [GO:0003723] and oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491] were the most enriched in samples from individuals that survived COVID-19 (Suppl. Table 4). An analysis of the proteins underlying the SeqScreen GO term assignments showed that RNA binding [GO:0003723] was driven by an enrichment of 30S and 50S ribosomal proteins from the Gram-positive cocci belonging to the genera Streptococcus, Granulicatella, Enterococcus, and Lactococcus, all of which were particularly prevalent in the “nCov7” survived COVID-19 patient from the Shen et al. study (Suppl. Table 8). The enrichment of the oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491] term among survived COVID-19 patients was driven by many different samples and a variety of bacteria, including those from Gram-positive bacteria belonging to the genera Enterococcus, Streptococcus, Streptomyces, Pediococcus, Lactococcus, and Granulicatella. Examples of underlying reference proteins to which reads mapped resulting in our observed oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491] term included quinone oxidoreductase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Suppl. Table 14). Among the deceased COVID-19 patients, the terminal GO terms of endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175], zinc ion binding [GO:0008270], and nucleobase-containing compound biosynthetic process [GO:0034654] were being driven by an enrichment of SARS-CoV-2 proteins (Suppl. Tables 10, 12, 14). Mixed among proteins from other organisms, an enrichment of Variovorax proteins tagged with the terminal GO terms of pyrimidine-containing compound biosynthetic process [GO:0072528] (e.g., CTP synthase, putative sulfonate/nitrate transport system substrate-binding protein), organonitrogen compound catabolic process [GO:1901565] (e.g., histidine ammonia-lyase, aspartate/glutamate leucyltransferase), magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287] (e.g., proteins involved in the histidine biosynthesis pathway, such as phosphoribosyl-AMP cyclohydrolase), and DNA recombination [GO:0006310] (e.g., inclusive of possible Variovorax phage proteins—integrase family protein, putative transposase IS4 family, phage integrase family protein) appeared in the COVID-19 deceased patients. This enrichment of Variovorax proteins among samples from individuals who died of COVID-19 was consistent with the results from the taxonomic comparison analysis. Compared to the survived group, the taxonomic comparisons in the deceased group revealed a statistically significant (p < 0.0001, q < 0.001) increase of the family Comamonadaceae, belonging to the genus Variovorax, and decreases in the family Bacteriodales (Fig. 4, Table 6).
Heat tree demonstrating the BALF metatransciptome profiles associated with COVID-19 mortality. Taxa colored in red were more prevalent amongst COVID-19 patients who died, and nodes in blue represent taxa that were more prevalent amongst patients who survived COVID-19. Notable increases were observed in the log2 median ratios in the family Comamonadaceae, genus Variovorax, and significant decreases in the log2 median ratios of order Bacteroidia and class Bacteroidales.